t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbour Embedding (tSNE)
Interested? Contact muehlhaus@bio.uni-kl.de or venn@bio.uni-kl.de
Table of contents
Introduction
- tSNE is a dimensionality reduction method. It allows you to visualise a multi-dimensional dataset in 2 or 3 dimensional scatter plot. But what does that mean in practice? Imagine you measured height, weight, width, density, brightness, as well as magnetic, chemical, and physical properties of a bunch of objects. The simplest technique to summarize your measurements is a spreadsheet table in which each row represents an element, and each column represents a measured feature:
Object ID |
height |
weight |
width |
density |
brightness |
magnetic field |
... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
objectA |
2 |
30 |
3 |
2 |
200 |
100000 |
... |
objectB |
4 |
50 |
2 |
3 |
255 |
130000 |
... |
objectC |
15 |
20 |
1 |
2 |
11 |
10000000 |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
- Note that the measured features span multiple orders of magnitude. A change of 1 in height for example has much more value than a change of 1 regarding the magnetic field. If now clusters of similar behaving objects should be identified, you are limited to inspect the data set column-wise by repetitive sorting. Just from the table you cannot create a meaningful graph, that allows you to perform a visual inspection of all features at once. Like principal component analysis (PCA), tSNE is a method for dimensionality reduction. It aggregates all features to a feature subset that allows a visual inspection of the complex data. It often is applied in image processing, NLP, genomic data, and speech processing.
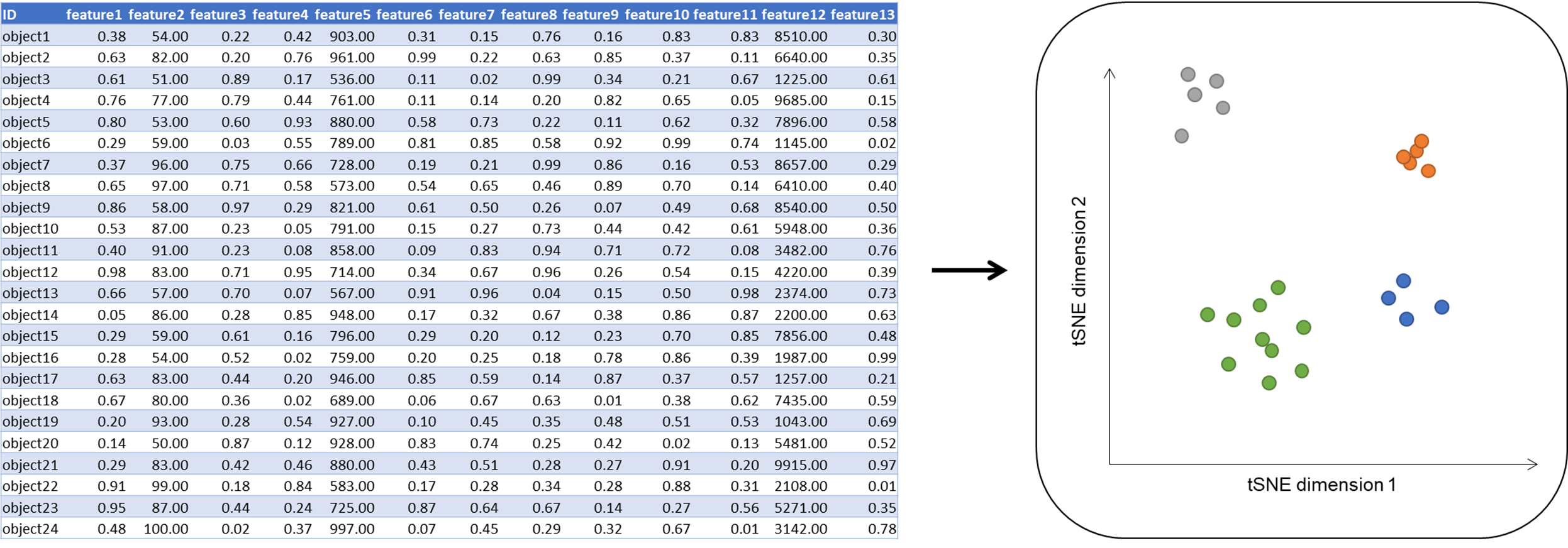 Fig. 1: Idea of tSNE. Visualisation of a high dimensional data on a 2-dimensional scatter plot.
Fig. 1: Idea of tSNE. Visualisation of a high dimensional data on a 2-dimensional scatter plot.
Aim for this project
- Blog post introducing the method, its applications, and limitations.
- Implement t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbour Embedding in FSharp.Stats.
Coding clues
Notes:
- All functions below are taken from the original publication (van der Maaten and Hinton 2008).
- Be aware, that the original work first describes SNE and later (section 3) describes the differences made to result in t-SNE!
- Although variance is continually referred to as σi in the paper, that is a repeated typo and should be σi2.
- The data matrix has n rows (without header row). The first index defines the row, the second the column!
- xi defines the ith row in the data matrix (a vector of measured features).
||x|| indicates the vector norm, in this case it is the Euclidean distance between vector xi and yi. You can find distance metrics at
FSharp.Stats.ML.DistanceMetrics.- exp(t) indicates et
- A t distribution with degree of freedom = 1 is equal to 0.3183*(1+t²)-1 where the first constant part can be neglected if the constant term exists in all calculations.
Pseudocode:
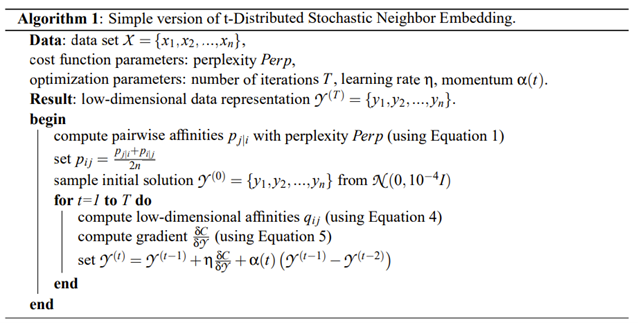
0th step:
- Read the publication and visit further introduction material you can find below (References)
1st step:
create a F# script (.fsx), load and open
FSharp.Stats,FSharpAux, andPlotly.NET-
import test data
You can find the classic clustering dataset "iris" here.
#r "nuget: FSharp.Stats, 0.4.1"
#r "nuget: Plotly.NET, 2.0.0-beta9"
open FSharp.Stats
open Plotly.NET
let fromFileWithSep (separator:char) (filePath) =
// The function is implemented using a sequence expression
seq { let sr = System.IO.File.OpenText(filePath)
while not sr.EndOfStream do
let line = sr.ReadLine()
let words = line.Split separator//[|',';' ';'\t'|]
yield words }
let lables,data =
fromFileWithSep ',' (__SOURCE_DIRECTORY__ + "../content/irisData.csv")
|> Seq.skip 1
|> Seq.map (fun arr -> arr.[4], [| float arr.[0]; float arr.[1]; float arr.[2]; float arr.[3]; |])
|> Seq.toArray
|> Array.shuffleFisherYates
|> Array.mapi (fun i (lable,data) -> sprintf "%s_%i" lable i, data)
|> Array.unzip
2nd step:
Calculate a Euclidean distance matrix using
ML.DistanceMetrics.euclidean. The matrix’ dimensions are n x n.-
Define functions that calculate similarity measures using the prior defined distance matrix:
-
(1) high dimensional affinity p (pi|j)(Equation 1)
- Inform yourself how the variance is determined. If required define a Perplexity beforehand.
- (2) low dimensional affinity q (qij) (Equation 4)
-
3rd step:
-
Calculate the high dimensional affinity matrix between every data pair.
- Note: pij ≠ pi|j
- pij = (pj|i + pi|j) / 2n
- The matrix has the dimensions n x n . The similarity of a point to itself is 0.
4th step:
-
Create an initial solution y(0) so that:
- y(0) is a matrix (n x d)
- y(0) contains as many rows as the original data matrix has rows (n)
- The number of values in each row is the number of dimensions you want to obtain in the end (d; in most cases 1-3, but should be defined by user).
- Each value is a randomly sampled from a normal distribution with mean = 0 and var = 0.0001.
// defines a normal distribuiton with mean = 3 and stDev = 2
let normalDist = Distributions.Continuous.normal 3. 2.
let createInitialGuess n = Array.init n (fun x -> normalDist.Sample())
// see FSharp.Stats documentation for probability distributions in the first code block for details
// https://fslab.org/FSharp.Stats/Distributions.html#Normal-distribution)
5th step:
- Recursively loop from t=1 to T (number of iterations)
- calculate low dimensional affinities (qij (Equation 4)) for all low dimensional result vectors from 3rd step. Collect results in a matrix (n x n).
- compute gradient (Equation 5)
- calculate the updated result y(t) and repeat.
6th step:
- report y(T) as final result
7th step:
- Use a 2D and 3D scatter plot from Plotly.NET to visualize your result.
8th step: Function implementation in F#
-
create a function, that contains all necessary helper functions in its body and takes the following parameters (suggestion):
Parameter name
data type
description
data
matrixdatamatrix (cols=features, rows=elements)
dimensions
intnumber of dimensions the final output data points have
maxIter
intmaximal number of iterations
perplexity
floatinform yourself if the perplexity should be defined by the user, or is calculated within the algorithm
learnRate
floatinform yourself
momentum
floatinform yourself
- Default parameters should be given in the function description or as optional paramter.
References
van der Maaten & Hinton; Visualizing Data using t-SNE (2008) PDF
https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/Rtsne/Rtsne.pdf page 5
-
https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2017/01/t-sne-implementation-r-python/
- Note: Inform yourself if the variance in Step 4 is in fact based on t distribution or if at this point of the algorithm a standard gaussian normal distribution is used!
https://www.datacamp.com/community/tutorials/introduction-t-sne
Additional information
Testing
- Apply tSNE to a dataset of your choice.
- optional: Test your results against implementations in R/Python or in the best case against the datasets proposed in the original publication.
Blog post
- Don’t forget to describe the limits/weaknesses of the approach in your blog post.
- How to handle/preprocess ties?
- optional: Compare the method to PCA.
namespace FSharp
--------------------
namespace Microsoft.FSharp
val char : value:'T -> char (requires member op_Explicit)
<summary>Converts the argument to character. Numeric inputs are converted according to the UTF-16 encoding for characters. String inputs must be exactly one character long. For other input types the operation requires an appropriate static conversion method on the input type.</summary>
<param name="value">The input value.</param>
<returns>The converted char.</returns>
--------------------
[<Struct>] type char = System.Char
<summary>An abbreviation for the CLI type <see cref="T:System.Char" />.</summary>
<category>Basic Types</category>
val seq : sequence:seq<'T> -> seq<'T>
<summary>Builds a sequence using sequence expression syntax</summary>
<param name="sequence">The input sequence.</param>
<returns>The result sequence.</returns>
--------------------
type seq<'T> = System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable<'T>
<summary>An abbreviation for the CLI type <see cref="T:System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable`1" /></summary>
<remarks> See the <see cref="T:Microsoft.FSharp.Collections.SeqModule" /> module for further operations related to sequences. See also <a href="https://docs.microsoft.com/dotnet/fsharp/language-reference/sequences">F# Language Guide - Sequences</a>. </remarks>
<summary>Provides static methods for the creation, copying, deletion, moving, and opening of a single file, and aids in the creation of <see cref="T:System.IO.FileStream" /> objects.</summary>
<summary>Negate a logical value. Not True equals False and not False equals True</summary>
<param name="value">The value to negate.</param>
<returns>The result of the negation.</returns>
<summary>Gets a value that indicates whether the current stream position is at the end of the stream.</summary>
<exception cref="T:System.ObjectDisposedException">The underlying stream has been disposed.</exception>
<returns><see langword="true" /> if the current stream position is at the end of the stream; otherwise <see langword="false" />.</returns>
System.String.Split(separator: string [], options: System.StringSplitOptions) : string []
System.String.Split(separator: string,?options: System.StringSplitOptions) : string []
System.String.Split(separator: char [], options: System.StringSplitOptions) : string []
System.String.Split(separator: char [], count: int) : string []
System.String.Split(separator: char,?options: System.StringSplitOptions) : string []
System.String.Split(separator: string [], count: int, options: System.StringSplitOptions) : string []
System.String.Split(separator: string, count: int,?options: System.StringSplitOptions) : string []
System.String.Split(separator: char [], count: int, options: System.StringSplitOptions) : string []
System.String.Split(separator: char, count: int,?options: System.StringSplitOptions) : string []
module Seq from Plotly.NET
--------------------
module Seq from FSharp.Stats
<summary> Module to compute common statistical measure </summary>
--------------------
module Seq from Microsoft.FSharp.Collections
<summary>Contains operations for working with values of type <see cref="T:Microsoft.FSharp.Collections.seq`1" />.</summary>
<summary>Returns a sequence that skips N elements of the underlying sequence and then yields the remaining elements of the sequence.</summary>
<param name="count">The number of items to skip.</param>
<param name="source">The input sequence.</param>
<returns>The result sequence.</returns>
<exception cref="T:System.ArgumentNullException">Thrown when the input sequence is null.</exception>
<exception cref="T:System.InvalidOperationException">Thrown when count exceeds the number of elements in the sequence.</exception>
<summary>Builds a new collection whose elements are the results of applying the given function to each of the elements of the collection. The given function will be applied as elements are demanded using the <c>MoveNext</c> method on enumerators retrieved from the object.</summary>
<remarks>The returned sequence may be passed between threads safely. However, individual IEnumerator values generated from the returned sequence should not be accessed concurrently.</remarks>
<param name="mapping">A function to transform items from the input sequence.</param>
<param name="source">The input sequence.</param>
<returns>The result sequence.</returns>
<exception cref="T:System.ArgumentNullException">Thrown when the input sequence is null.</exception>
val float : value:'T -> float (requires member op_Explicit)
<summary>Converts the argument to 64-bit float. This is a direct conversion for all primitive numeric types. For strings, the input is converted using <c>Double.Parse()</c> with InvariantCulture settings. Otherwise the operation requires an appropriate static conversion method on the input type.</summary>
<param name="value">The input value.</param>
<returns>The converted float</returns>
--------------------
[<Struct>] type float = System.Double
<summary>An abbreviation for the CLI type <see cref="T:System.Double" />.</summary>
<category>Basic Types</category>
--------------------
type float<'Measure> = float
<summary>The type of double-precision floating point numbers, annotated with a unit of measure. The unit of measure is erased in compiled code and when values of this type are analyzed using reflection. The type is representationally equivalent to <see cref="T:System.Double" />.</summary>
<category index="6">Basic Types with Units of Measure</category>
<summary>Builds an array from the given collection.</summary>
<param name="source">The input sequence.</param>
<returns>The result array.</returns>
<exception cref="T:System.ArgumentNullException">Thrown when the input sequence is null.</exception>
module Array from FSharp.Stats
<summary> Module to compute common statistical measure on array </summary>
--------------------
module Array from Microsoft.FSharp.Collections
<summary>Contains operations for working with arrays.</summary>
<remarks> See also <a href="https://docs.microsoft.com/dotnet/fsharp/language-reference/arrays">F# Language Guide - Arrays</a>. </remarks>
<summary> Shuffels the input array (method: Fisher-Yates) </summary>
<summary>Builds a new array whose elements are the results of applying the given function to each of the elements of the array. The integer index passed to the function indicates the index of element being transformed.</summary>
<param name="mapping">The function to transform elements and their indices.</param>
<param name="array">The input array.</param>
<returns>The array of transformed elements.</returns>
<exception cref="T:System.ArgumentNullException">Thrown when the input array is null.</exception>
<summary>Print to a string using the given format.</summary>
<param name="format">The formatter.</param>
<returns>The formatted result.</returns>
<summary>Splits an array of pairs into two arrays.</summary>
<param name="array">The input array.</param>
<returns>The two arrays.</returns>
<exception cref="T:System.ArgumentNullException">Thrown when the input array is null.</exception>
<summary> Initializes a Normal distribution </summary>
<summary>Creates an array given the dimension and a generator function to compute the elements.</summary>
<param name="count">The number of elements to initialize.</param>
<param name="initializer">The function to generate the initial values for each index.</param>
<returns>The created array.</returns>
<exception cref="T:System.ArgumentException">Thrown when count is negative.</exception>